TKK | Tietoverkkolaboratorio | Julkaisut
Annual Report 1998: Preface | Introduction | Personnel | Research projects | Teaching | Activities | Participation in boards and committees | Publications
The course "Introduction to teletraffic theory" (S-38.145) was given for the first time in spring 1998. The course is planned to give a broad view of teletraffic issues in communications networks and familiarise the students with the basic tools for the dimensioning and analysis of the networks. Most of the material of the course is available in electronic form.
The course "Simulation of telecommunications networks" (S-38.147), was given for the first time in fall 1999. The course consists of three parts. In the first part general aspects of simulation are addressed and different methods for the generation of random variables and statistical analysis of the results are introduced. The second part deals with the construction of an event based simulation program. The third part gives an introduction to the available commercial simulation tools and a more detailed look at a specific tool.
The contents of the optional course "Principles in communication engineering" (S-38.105) was largely renewed. The course is now an overview of telecommunications and its purpose is to provide guidelines and pointers for further studies. The main body of work for the course book "Tietoliikenneaapinen" was completed during the year by Kirsi Voipio and Seppo Uusitupa.
The contents of the course Telecommunications Technology II was partially renewed. The course is now totally devoted to routing in packet and circuit switched networks.
The laboratory has given education in 25 courses. The courses can be divided into 7 groups:
S-38.105 Principles in Communication Engineering (Tietoliikennetekniikan
perusteet)
S-38.118 Principles in Telecommunications Technology (Teletekniikan
perusteet)
S-38.117 Seminar on Telecommunications Technology (Teletekniikan seminaari)
S-38.188 Telecommunication Networks (Tietoliikenneverkot)
S-38.191 Corporate Networks (Televerkot yrityksissä)
S-38.110 Telecommunication Switching Technology I (Tiedonvälitystekniikka I)
S-38.122 Telecommunication Switching Technology II (Tiedonvälitystekniikka II)
S-38.164 Broadband Switching Technology (Laajakaistainen välitystekniikka)
S-38.166 Programming of Telecommunication Switching Systems (Televälitysjärjestelmien
ohjelmointi)
S-38.211 Signal Processing in Telecommunications I (Signaalinkäsittely
tietoliikenteessä I)
S-38.212 Signal Processing in Telecommunications II (Signaalinkäsittely
tietoliikenteessä II)
S-38.001 Telecommunications Forum (Telecommunications Forum)
S-38.130 Postgraduate Course in Telecommunications (Teletekniikan lisensiaattikurssi)
S-38.141 Teletraffic Theory (Teleliikenneteoria)
S-38.143 Queueing Theory (Jonoteoria)
S-38.149 Postgraduate Course in Teletraffic Theory (Teleliikenneteorian
lisensiaattikurssi)
S-38.200 Individual Course in Telecommunications (Teletekniikan yksilöllinen
opintojakso)
S-38.220 Licentiate Course in Signal Processing in Communications (Tietoliikenteen
signaalinkäsittelyn lisensiaattikurssi)
S-38.350 Research Seminar on Telecommunications Technology (Teletekniikan
tutkijaseminaari)
S-38.145 Introduction to Teletraffic Theory (Liikenneteorian perusteet)
S-38.147 Simulation of Telecommunication networks (Televerkkojen simulointi)
S-38.123 Telecommunications Technology, laboratory course I (Teletekniikan
laboratoriotyöt I)
S-38.124 Telecommunications Technology, laboratory course II (Teletekniikan
laboratoriotyöt II)
S-38.128 Telecommunications Technology, special assignment (Teletekniikan
erikoistyö)
S-38.300 Thesis Seminar on Telecommunications Technology (Teletekniikan
diplomityöseminaari)
Marko Silventoinen: Indoor GSM base station systems
The thesis of Marko Silventoinen studies indoor GSM base station systems. The indoor environment can be divided into two parts, home and office.
At home the subscriber can be given the possibility to invest in his or her own infrastructure by offering a low-cost Home Base Station (HBS). This will allow the GSM operator to apply lower rates at calls made from home, thus challenging the fixed line operator. An MS based hardware architecture will be used to achieve the low costs required from a consumer product. This leads to modifications on the air interface. In this thesis Silventoinen has studied two aspects of the HBS air interface: a frequency hopping scheme that allows HBSs to share the spectrum with the overlaying GSM network, and a fast power control scheme that helps HBSs to increase their performance without frequency hopping capability.
In the near future the shortage of carrier frequencies at the GSM band will force the operators to look for possibilities to enhance GSM's spectral efficiency, especially in already congested urban areas. The studies performed on the office BTS address this problem and propose new ways to improve the spectral efficiency while maintaining the air interface compatibility with the existing handsets.
The proposed indoor GSM base station concepts can serve also in other environments: HBS in small offices, and office BTS in shopping malls, stadiums, or even as a generic hot-spot solution.
Samuli Aalto: Studies in queueing theory
The thesis of Samuli Aalto consists of two parts. In Part I, the optimal control problem of batch service queueing systems is studied. A natural control problem involves the determination of the epochs at which the service is initiated as well as the sizes of the batches served. The case of finite service capacity with general holding costs is considered with two types of arrival processes (Poisson and compound Poisson). In each case a new class of operating policies is introduced and it is proven that, under some additional assumptions, there is an optimal operating policy belonging to this new class. Models of this kind have applications, for example, in the area of transportation systems
In Part II the output process of some fluid flow storage models are characterized. First, assuming that the input rate is modulated by a certain type of a Markov jump process, it is proven that there exists another Markov jump process that modulates the output rate. The modulating process is explicitly constructed. Second, a fluid model of a multiplexer loaded by a finite number of heterogenerous on-off sources is considered. The main result here is a generalization of an earlier result characterizing the active periods on the output line by means of Laplace transforms.
| 1. Aaltonen S. | The optimization of the creation of management applications for the intelligent networks, in Finnish (Hallintasovellusten luonnin optimointi älyverkon palvelun-hallinnassa) | NTC |
| 2. Aromaa A. | Mid-sized company's network and the evolution of it, in Finnish (Keskikokoisen yrityksen lähiverkko ja sen kehittäminen) | TIE |
| 3. Bäckström M. | Interworking concepts for computer supported corperative work applications in a heterogeneous network, in Finnish (Ryhmätyösovellusten yhteiskäyttö heterogeenisessä verkkoympäristössä) | HPY |
| 4. Eronen H. | Mobile and secure access to corporate intranet | TWG |
| 5. Haaksiala A. | A descriptive method of interoperability for distributed information systems, in Finnish (Menetelmä hajautettujen tietojärjestelmien yhteistoiminnallisuuden kuvaamiseksi) | NTC |
| 6. Heikkinen T. | Information flow in internal trade, in Finnish (Tiedonsiirto yrityksen sisäisessä kaupankäynnissä) | F-ICLC |
| 7. Helsingius M. | Service level management and application response time measurement in a client/server environment | HP |
| 8. Huopaniemi J. | The use of GSM-based protocols in intelligent network, in Finnish (GSM-protokollien käyttö älyverkon palvelukehityksessä) | SON |
| 9. Huostila T. | The requirements on and advantages of the optimal routing of GSM calls from the point of view of a teleoperator, in Finnish (GSM-puheluiden optimaalisen reitityksen vaatimukset ja hyödyt teleoperaattorin kannalta) | SON |
| 10. Hänninen M. | The short message transfer capacity optimization using TCP/IP protocol, in Finnish (Lyhytsanomavälityksen optimointi TCP/IP-protokollan avulla) | NTC |
| 11. Iisakkila K. | Air interface interoperability of network layer services in TETRA mobile radio networks, in Finnish (Verkkokerrospalvelujen yhteensopivuus TETRA-erillisradioverkon ilmatierajapinnassa) | NTC |
| 12. Iraji S. | Preprocessor software platform design for Nokia DX200 system | NTC |
| 13. Jaatinen A. | Charging in the permanent and switched ATM networks, in Finnish (Veloitus kiinteässä ja kytkentäisessä ATM-verkossa) | DAT |
| 14. Kahanpää H. | The implementation of CTI functions to subscribers of an EWSD exchange, in Finnish (Tietokoneen ja puhelimen yhteiskäyttötoiminteiden toteuttaminen EWSD-keskuksen tilaajille) | SIE |
| 15. Kanerva J. | The development and the commercializing of one digital announcer, in Finnish (Digitaalisen tiedotuslaitteen kehitys ja tuotteistus) | MUUT |
| 16. Kaseva M. | Implementing network supplementary services into intelligent networks, in Finnish (Älyverkon käyttö tilaajatoiminteiden toteuttamisessa) | SON |
| 17. Kehä M. | Improving network performance for a workstation cluster | NRC |
| 18. Koivisto E. | Feasibility of data communications services on the ISDN D-channel | NTC |
| 19. Koski J. | GSM service evolution towards universal mobile telecommunications system | SON |
| 20. Kuusivaara J. | Production testing of broadband interface modules, in Finnish (Laajakaistaisten tietoliikennemoduulien tuotantotestaus) | TE |
| 21. Laamanen M. | Extranet application in telecom customer services | LME |
| 22. Laamanen P. | The use of unifield modeling language in intranet project, in Finnish (UML-kuvauskielen käyttö Intranet-projektissa) | SPY |
| 23. Laitala K. | Subscriber segmentation in mobile networks | NTC |
| 24. Lehtonen J. | Energy company's customer reporting system, in Finnish (Energiayhtiön asiakasraportointijärjestelmä) | TUE |
| 25. Lehtovirta V. | Internet protocol switching in cellular access networks | LME |
| 26. Leinonen M. | Applying OCTOPUS-method to DX 200 -systems hardware configuration management, in Finnish (Octopus-menetelmän soveltaminen DX200-järjestelmän laitteisto-konfiguraation hallintaan) | NTC |
| 27. Liu J. | China's telecommunications market and Technomen's operation - a case study | TM |
| 28. Mensola S. | Communication management in IP-based networks, in Finnish (IP-verkon kommunikaatiopalveluiden hallinta) | HPY |
| 29. Merikoski M. | Distance education through the world wide web | CERN |
| 30. Miikkulainen J. | Automation of the hardware configuration management of a distributed system | NTC |
| 31. Peltonen L. | Software process measurement and improvement: a case study in telecommunications | NTC |
| 32. Peräläinen I. | Labelbased multilayer routing, in Finnish (Leimapohjainen monikerrosreititys) | HUT |
| 33. Rosqvist T. | Modernisation of an automatic fire alarm system, in Finnish (Erään automaattisen paloilmoitinjärjestelmän uudistaminen) | NES |
| 34. Rostas P. | Architecture for web based Information services in GSM networks | SON |
| 35. Räsänen P. | Screening as a part of security of common channel signalling, in Finnish (STP-liikenteen käyttörajoitukset osana yhteiskanavamerkinannon turvallisuutta) | NTC |
| 36. Saukko T. | Simulator testing of ISDN user part in mobile networks, in Finnish (ISDN-käyttäjäosan simulaattoritestaus matkapuhelinverkoissa) | SIE |
| 37. Sipilä J. | Application of external intelligent peripherals to mobile networks | SIE |
| 38. Teppo I. | Future development of the short message service | TM |
| 39. Timonen P. | The co-operation of the short message service with other services of GSM network, in Finnish (Lyhytsanomapalvelun yhteistoiminta GSM-verkon muiden palveluiden kanssa) | SON |
| 40. Xie D. | Design of optimal digital FIR pulse shaping filters for digital subscriber lines | HUT |
| 41. Yletyinen T. | The quality of voice over IP | HUT |
| CERN | European Laboratory for Particle Physics |
| DAT | Datatie Oy |
| F-ICLC | Fujitsu-ICL Computers |
| HP | Hewlett-Packard Oy |
| HPY | Helsinki Telephone Company |
| HUT | Helsinki Univ. of Technology/ Lab. of Telecom. Technology |
| LME | Oy L M Ericsson Ab |
| MUUT | Independent research |
| NES | Neste Oy |
| NRC | Nokia Research Center |
| NTC | Nokia Telecommunications |
| SIE | Siemens Finland |
| SON | Sonera |
| SPY | Savonlinnan puhelinyhdistys |
| TE | Tellabs Oy |
| TIE | Tieturi |
| TM | Tecnomen Oy |
| TUE | Turku Energia |
| TWG | Team WARE Group |

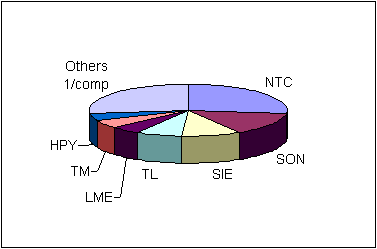
Figure 6: Employers of Masters students
Annual Report 1998: Preface | Introduction | Personnel | Research projects | Teaching | Activities | Participation in boards and committees | Publications
Networking laboratory is now part of Department of Communications and Networking. Content on this page may be obsolete.
|
This page is maintained by
and
Webmaster.
Last update on the page 07.03.2006 13:34. URL: http://www.netlab.tkk.fi/julkaisut/annual/1998/chapt4.shtml [ TKK > Electrical and Communications Engineering > Networking Laboratory > Publications ] |